Recruitment metrics are the key to measuring the effectiveness of your hiring efforts and building your talent acquisition strategy. When digging into your recruitment data, analysing metrics a combination of recruitment metrics will paint a full picture to identify where you need to focus your efforts and drive better results.
Check out our handy guide below on the key types of recruitment metrics, their definitions, and how to calculate them:
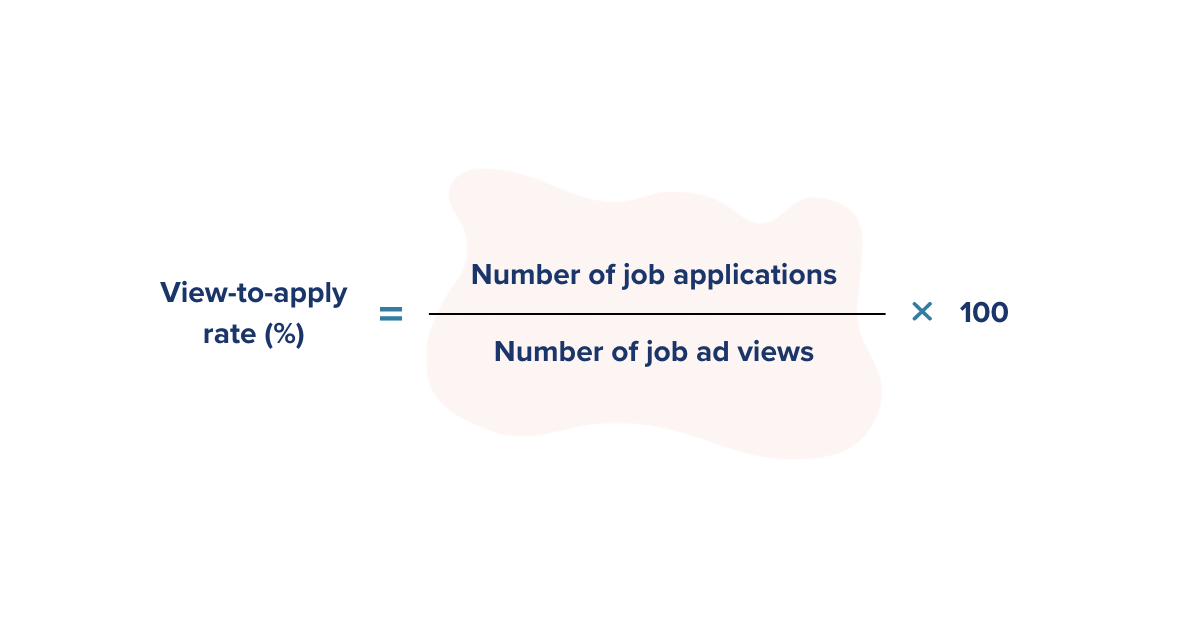
1. View-to-Apply Rate
The view-to-apply rate is used to calculate the percentage of job seekers who viewed your job advertisement and applied for the position. This allows you to assess how well your job ad is performing at enticing and converting candidates to take the next step and apply for the role.
2. Application Drop-off Rate
The application drop-off rate is the percentage of candidates who have started an application but failed to complete the application. A high drop-off rate may indicate a need to improve the candidate experience during the application process.

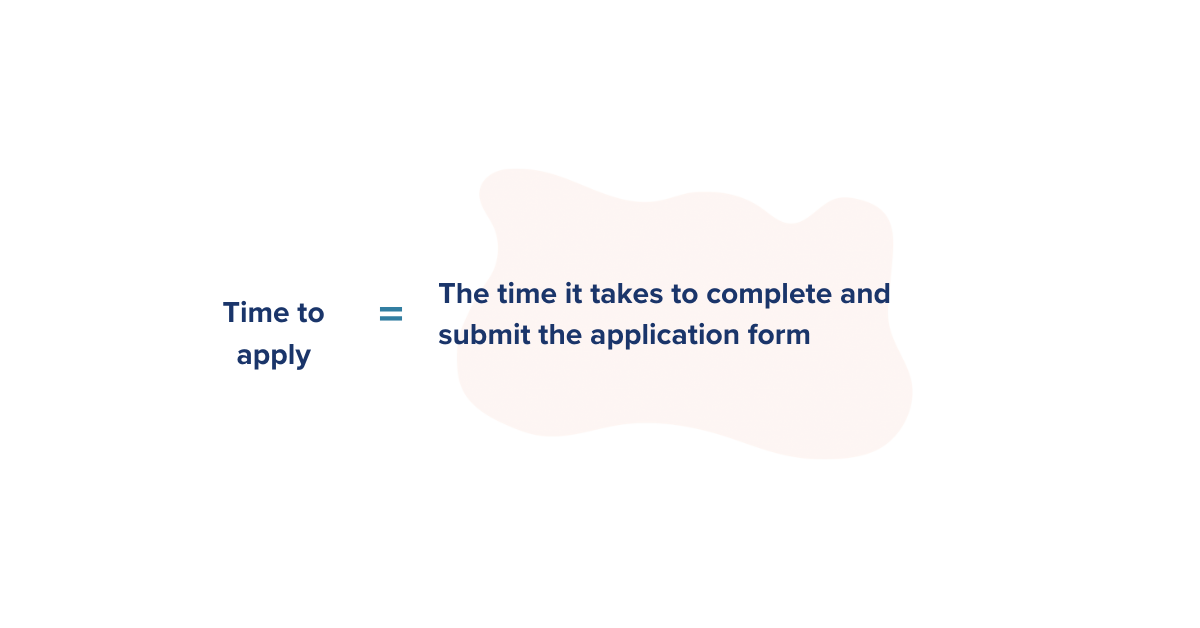
3. Time-to-Apply
The time-to-apply metric measures from the moment a candidate starts an application to the moment they click submit and complete their application. The shorter and more seamless the application process correlates with increased applications. A lengthy process can impact your candidate experience, especially on mobile, and runs the risk of losing out on applicants.
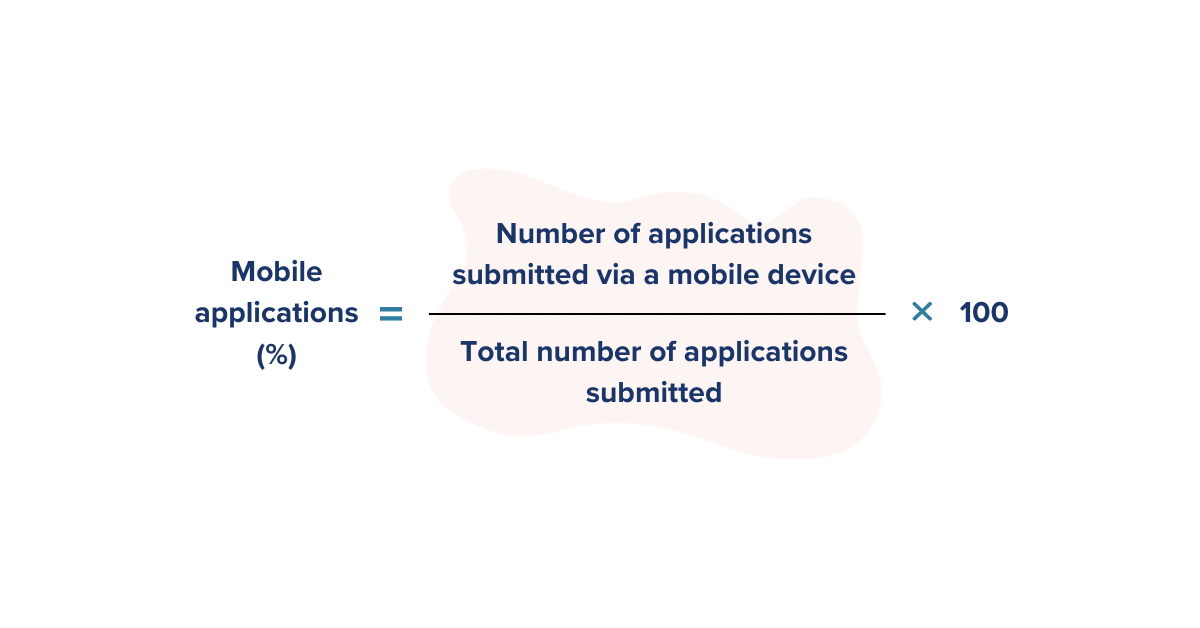
4. Mobile Applications
Tracking the percentage of mobile applications received against other devices can allow you to assess how effective the mobile application process is and optimise accordingly. Our research shows a strong correlation between time-to-apply and incomplete applications on mobile. As the application process lengthens, the number of incomplete applications on mobile increases.
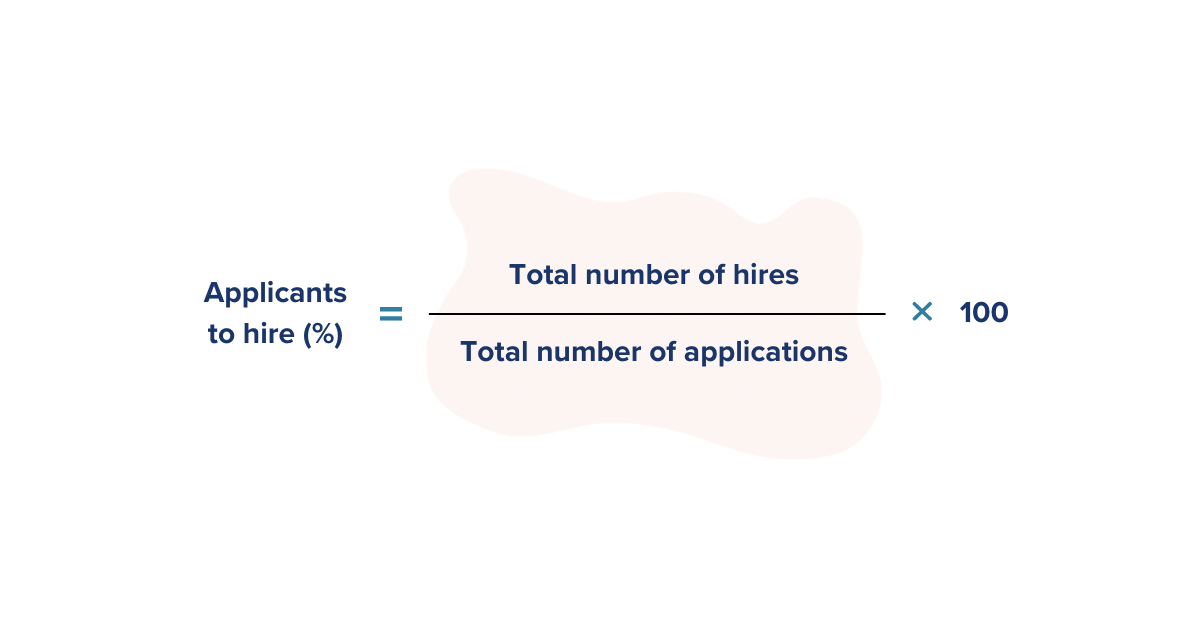
5. Applicant-to-Hire
The applicant-to-hire metric shows you how effective your job listings are. It can help you to identify whether your job listings are reaching and engaging the right audience based on the percentage of applicants who are converting to new hires.
6. Candidate-to-Hire
This metric demonstrates how many candidates are needed to find 1 hire. A low candidate to hire percentage shows that a lot of unsuccessful candidates are being presented to hiring managers, which can be costly, time consuming, and impact your employer brand.

7. Sourcing Channel Effectiveness
Sourcing channel effectiveness shows the percentage of applications that have resulted in new hires from a specific sourcing channel. This lets you identify the most effective channels at finding the talent for your organisation and where you should prioritise your efforts.

8. Sourcing Cost per Hire
Sourcing cost per hire calculates the cost efficiency of your different sourcing channels by dividing the advertising cost per source by the number of new hires per source. This allows you to analyse what channels are the best return on investment.

9. Offer Acceptance Rate
The offer acceptance rate highlights the percentage of offers made to candidates that have been accepted. This allows you to evaluate if your compensation is competitive, if you are an employer of choice, how attractive your offers are and if your compensation and benefits are competitive.

10. Time to Fill
The number of days taken from a new position getting approved within your organisation until the position is filled. Tracking the time to fill highlights your ability to find the right candidate and can help identify sourcing channel inefficiencies.

11. Time to Hire
The number of days taken from when the hired candidate applied for a job and entered the recruitment pipeline, until they accepted the offer. The time to hire highlights the speed in which you were able to identify a suitable candidate and progress them through your recruitment process.

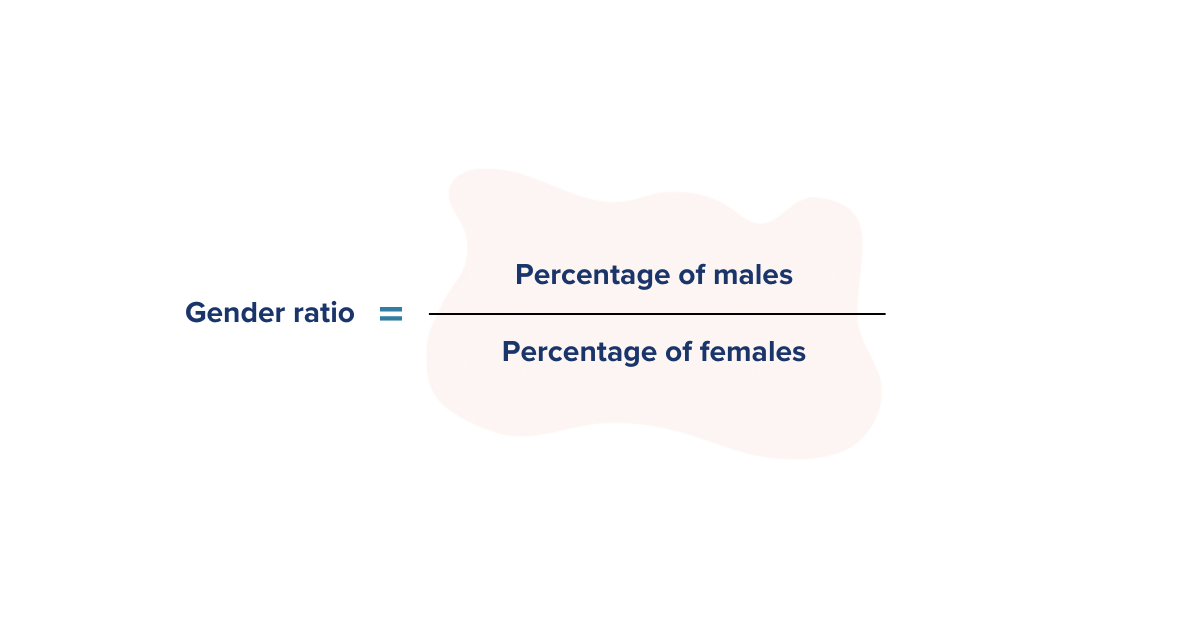
12. Gender Breakdown
Gender breakdown is a diversity metric that allows you to measure the gender ratio of career site visitors, applicants or new hires. This can help you assess your effectiveness at achieving your diversity goals and identify any potential issues or biases within your recruitment process.
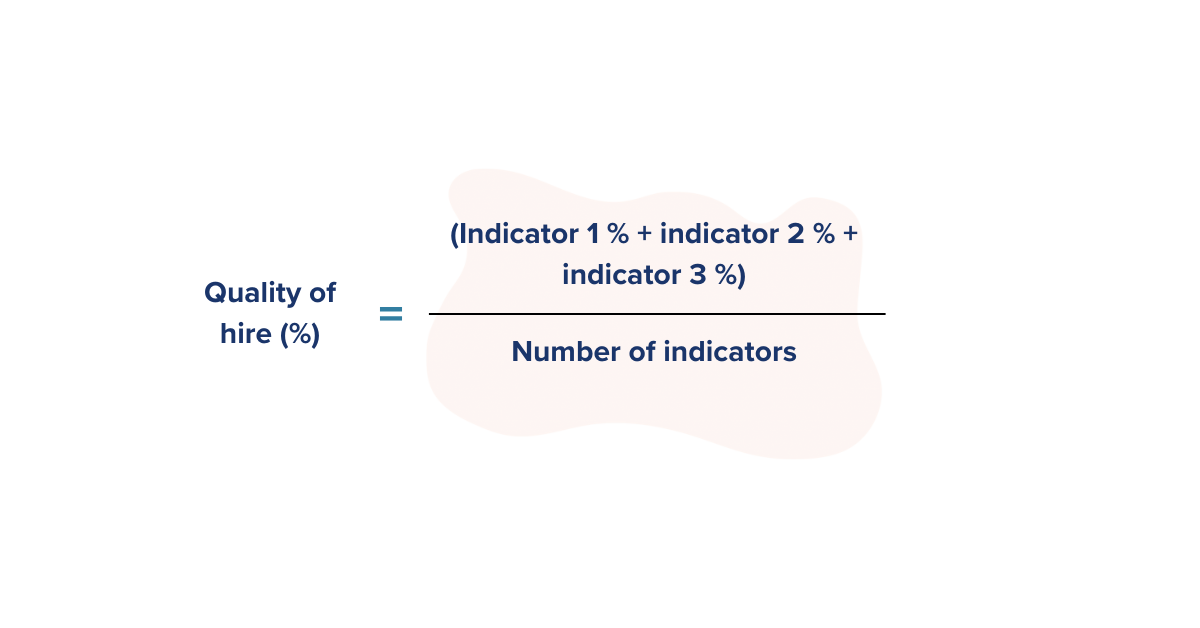
13. Quality of Hire
Quality of hire measures the value a new hire has brought to the organisation over time. It can help you evaluate the long-term effectiveness of your recruitment efforts in finding high quality talent for your organisation. QoH encompasses several different employee metrics, often called “indicators”, based on the organisational goals. Factors that contribute to the quality of hire include technical and soft skills, cultural fit, time-to-productivity and growth potential within the organisation.
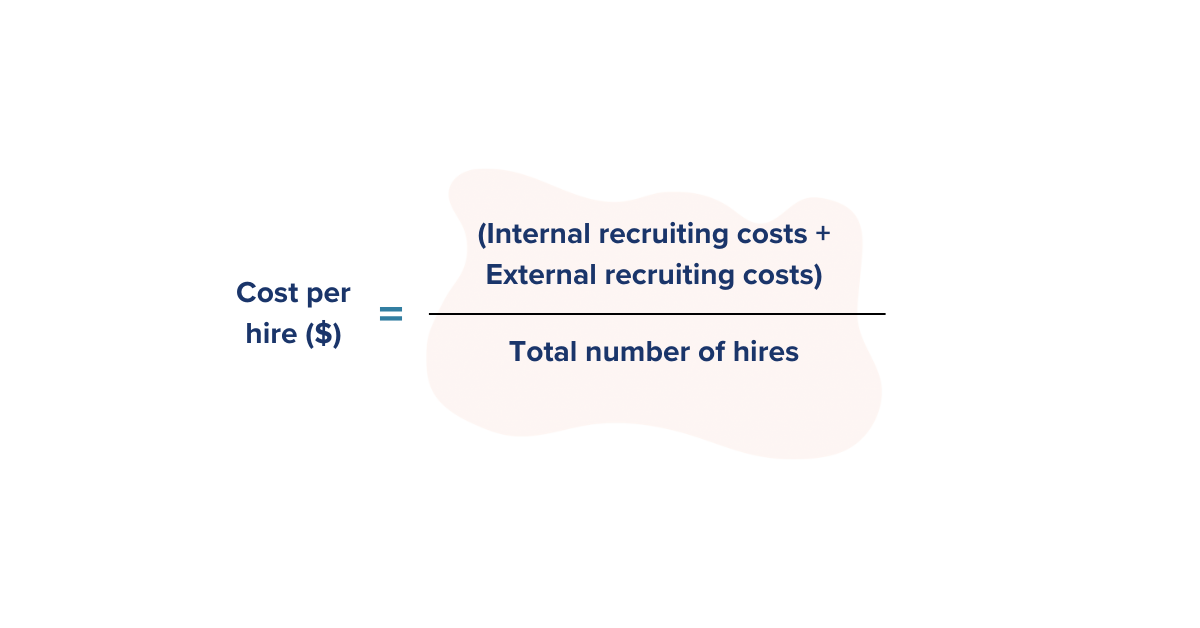
14. Cost per Hire
The cost per hire measures the amount spent on recruitment, from attraction to offer, over a given period, divided by the amount of new hires. Taking into account internal costs such as administrative, employee salaries and hiring manager time, as well as, external costs such as sourcing channels, background checks, and travel expenses.
15. Fill Rate
The fill rate determines how many jobs have been filled by your recruitment team over a specific period compared to the number of open jobs. This helps talent acquisition teams assess the effectiveness of filling vacancies and work towards reducing the number of open roles at any given time.

Tracking a combination of recruitment metrics that aligns with your organisation’s objectives will help you to evaluate and promote your recruitment ROI. PageUp analytics provides you with access to real-time data through intuitive dashboards with ease.
Learn more about how you can level up and use key metrics to boost your talent acquisition strategy here.






